
Forged hex bushing is a pipe fitting used in the pipe connection system. It mainly connects pipes of different diameters or different thread types, and plays a transition and conversion function in the pipe system. In the pipe system, when the diameter of the pipe needs to be changed, the threaded hexagonal bushing can be used to achieve it.
Due to its unique structure and function, the forged hex bushing is widely used in various industrial fields, such as power station supporting projects, seawater treatment, steam transmission, hot and cold water supply, oxygen transportation, fuel gas engineering, medical gas supply, chemical industry, oil refining, metallurgy, medicine and other industries.
Specification of Forged Hex Bushing
| Size Range | 1/8″, 1/4″, 3/8″, 1/2″, 3/4″, 1″, 1 1/4″, 1-1/2″, 2″, 2-1/2″, 3″, 4″ |
| Pressure Rating | Class 3000 |
| Standard | ASME B16.11, BS3799 |
| Thread Type | NPT, PT, BSPP, BSPT, PF |
| Carbon Steel Grades | ASTM A105 / A105N, ASTM A350 LF2 / LF3 |
| Alloy Steel Grades | ASTM A182 F11 / 12 / 5 / 9 / 91 / 92 / 22 |
| Stainless Steel Grades | ASTM A182 F304/304L/304H, 316/316L, 310S, 317, 347, 904L, 321 |
| Duplex Stainless Steel Grades | ASTM A182 F51, F53, F44 |
ASME B16.11 Hex Bushing Dimensions
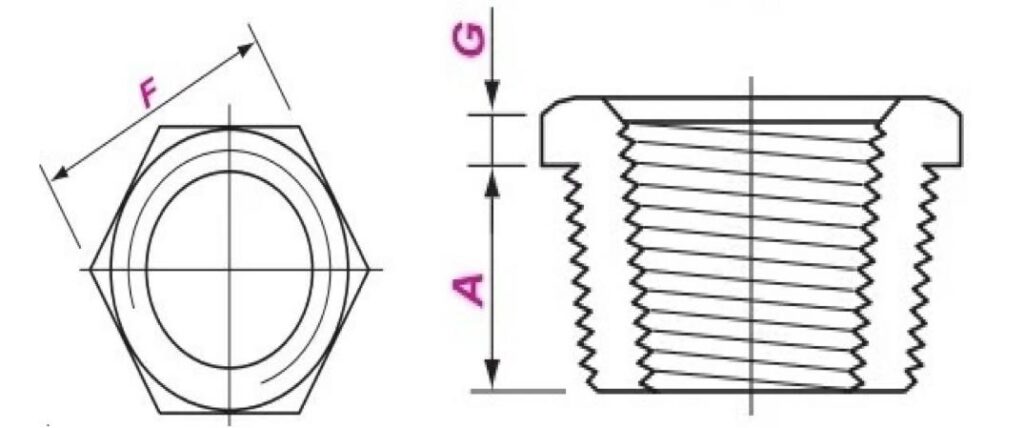
| Nominal Size | Length | Hex Height | Hex Width Flats | |
| DN | NPS | Amin | Gmin | Fnom |
| 6 | 1/8 | 10 | – | 11 |
| 8 | 1/4 | 11 | 3 | 16 |
| 10 | 3/8 | 13 | 4 | 18 |
| 15 | 1/2 | 14 | 5 | 22 |
| 20 | 3/4 | 16 | 6 | 27 |
| 25 | 1 | 19 | 6 | 36 |
| 32 | 11/4 | 21 | 7 | 46 |
| 40 | 11/2 | 21 | 8 | 50 |
| 50 | 2 | 22 | 9 | 65 |
| 65 | 21/2 | 27 | 10 | 75 |
| 80 | 3 | 28 | 10 | 90 |
| 100 | 4 | 32 | 13 | 115 |
Hex Bushing Material and Grades
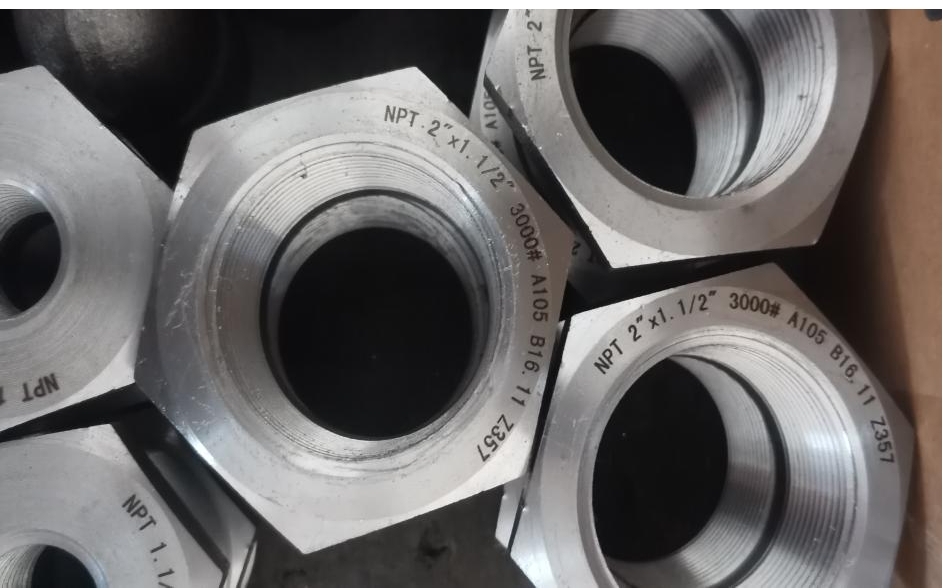
Carbon Steel Forged Hex Bushing
ASTM A105/ A105N, ASTM A 350 LF 2/ LF3, A694 F42 / 46 / 52 / 56 / 65 / 70,ASTM A182 F5 / F9 / F11 / F12 / F22 / F91 / F92
Carbon steel forged hex bushings are mainly made of carbon steel, which has a moderate carbon content and good mechanical properties and processing performance. Carbon steel thread bushings are therefore characterized by high strength, good wear resistance, and strong corrosion resistance, and can meet the use requirements in various complex environments.

Stainless Steel Forged Hex Bushing
A182 F304/304L/304H – F316/316L – F317 – F310S – F321 – F347 – F904L
Stainless steel has certain strength and toughness. It can withstand certain pressure and tension, and is not easy to break or deform in the pipeline system. For example, in the water supply and drainage system of a building, when the water pressure fluctuates, the stainless steel threaded bushing can withstand this pressure change and ensure the stability of the pipeline connection.

Duplex Steel Forged Hex Bushing
A182 F51/53/55/60
Duplex stainless steel has good toughness. This toughness makes it not easy to break when it is impacted or vibrated. In some industrial equipment pipeline connections with vibration sources, such as the pipeline system of large compressors, duplex stainless steel forged hex bushing can adapt to the vibration environment and will not produce fatigue cracks due to long-term vibration, thereby ensuring the reliability of pipeline connections.
How to Install the Threaded Hex Bushing
Step 1 Appearance Inspection
Before installation, the threaded bushing and related pipe fittings need to be cleaned. Remove impurities such as oil, dust, rust, etc. on the surface. For new pipe fittings, there may be some oil or impurities left over from the production process, while for old pipe fittings, there may be rust or dirt.
Step 2 Installation Process
Manual screwing: At the beginning, slowly screw the threaded bushing into the thread of the pipe fitting by hand. This is to initially establish a threaded connection and to feel whether there is thread interference or other problems.
Tighten with tools: After manually screwing in a few turns, you can use tools such as wrenches or pipe clamps to further tighten the threaded bushing. During the tightening process, pay attention to the amount of torque applied. For forged hex bushing of different sizes and materials, the appropriate tightening torque has a certain range.
Step 3 Inspection After Installation
Appearance inspection:After installation, perform an appearance inspection on the threaded bushing and its connection parts again. Check for new scratches, deformation, or whether the sealing material has overflowed.
Sealing inspection:Depending on the type and requirements of the pipeline system, different methods of sealing inspection can be performed. For low-pressure water pipe systems, a simple water flow test can be performed to check for leaks.
Latest News
 02 8 月 2019Copper Nickel Flanges UNS C70600Zizi offers ISO certified copper nickel flanges, stores large quantity of Cu-Ni 90/10 weld neck flan...
02 8 月 2019Copper Nickel Flanges UNS C70600Zizi offers ISO certified copper nickel flanges, stores large quantity of Cu-Ni 90/10 weld neck flan...  29 7 月 2019Stainless Steel Buttweld Fittings ManufacturerZizi is stainless steel buttweld fittings manufacturer, we offer stainless steel pipe elbow, tee, ca...
29 7 月 2019Stainless Steel Buttweld Fittings ManufacturerZizi is stainless steel buttweld fittings manufacturer, we offer stainless steel pipe elbow, tee, ca...  19 7 月 2019Steel Pipe Nipple Types, Dimensions and MaterialsBasic pattern of steel pipe nipple is a short piece of pipe with threads at both end or at one end....
19 7 月 2019Steel Pipe Nipple Types, Dimensions and MaterialsBasic pattern of steel pipe nipple is a short piece of pipe with threads at both end or at one end....
